A distributed network of remote sensors for GNSS monitoring in terms of integrity, reliability and immunity of the signals from spoofing and interference
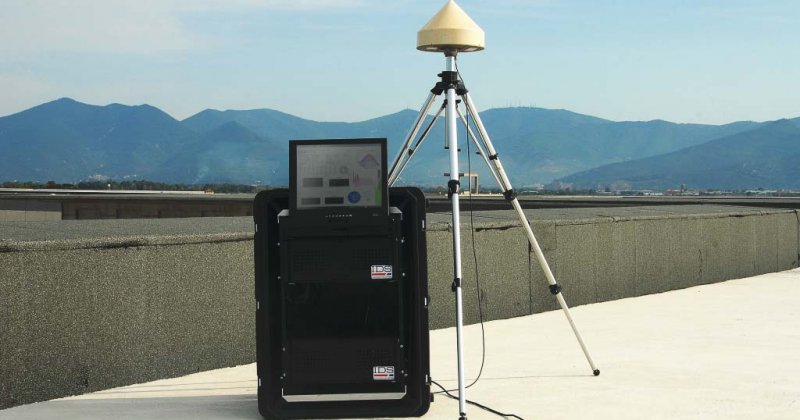
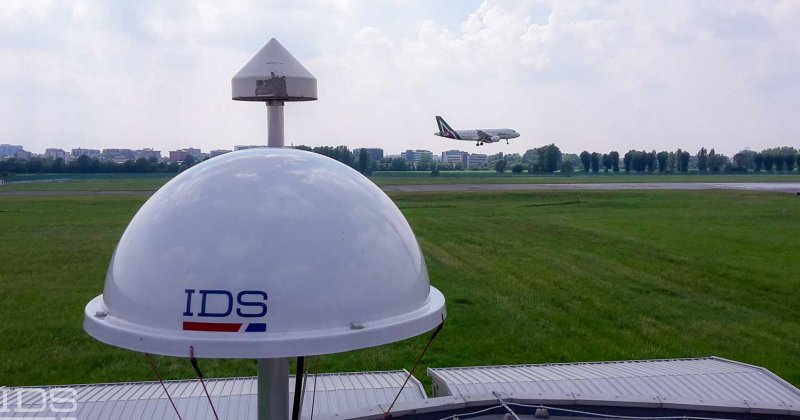
The GNOME (GNSS Operative Monitoring Equipment) system is a distributed network of remote sentinels designed to perform GNSS monitoring, especially in the vicinity of airports, in terms of integrity, reliability and the immunity of signals against spoofing and interference. The system is designed in response to the ICAO recommendations and standards which highly advise continuous control and legal recording of the GNSS performance and integrity, both in the signal and in the navigation domains.
The GNOME system has the flexibility and customizability to meet specific customer and user needs through the use of software-defined radio (SDR). It also includes receiver autonomous integrity monitoring (RAIM) prediction capabilities for the generation of GNSS NOTAM proposals and the creation of pilot briefings which can be accessed via a web portal.

The operational requirements and international standards that drove the development of GNOME come from the following regulations and guidelines related to GNSS operations:
- ICAO Annex 10, Volume 1
- ICAO Document 9849 (GNSS Manual)
- ICAO Doc 8071 Volume 2
- FAA Order 8200
Applications
GNOME - Main Benefits
GNOME – TECHNICAL SHEET
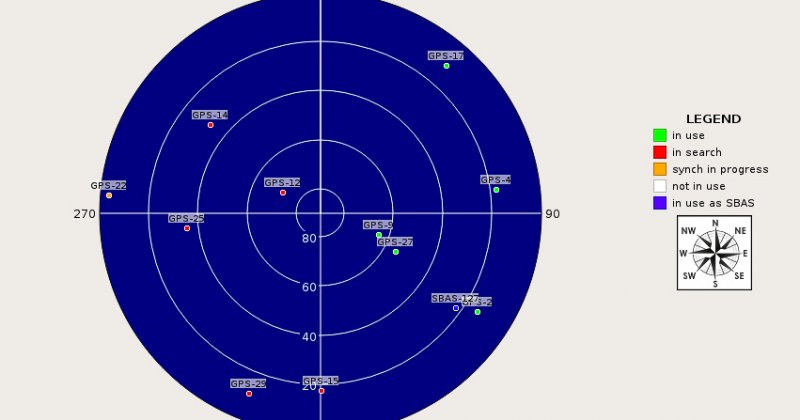
- Multi-band and multi-constellation GNSS Monitoring
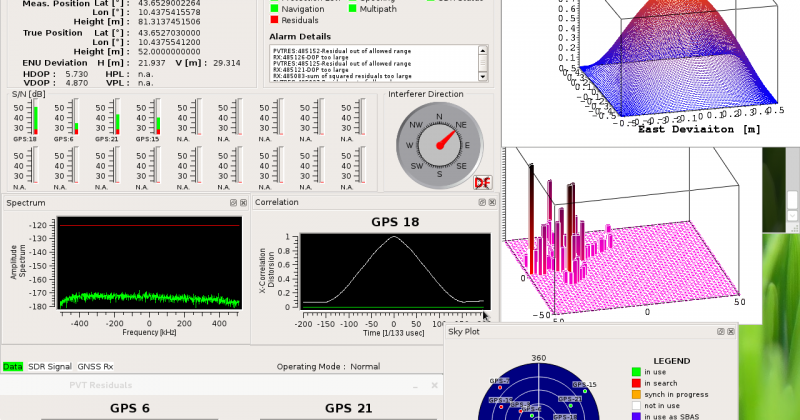
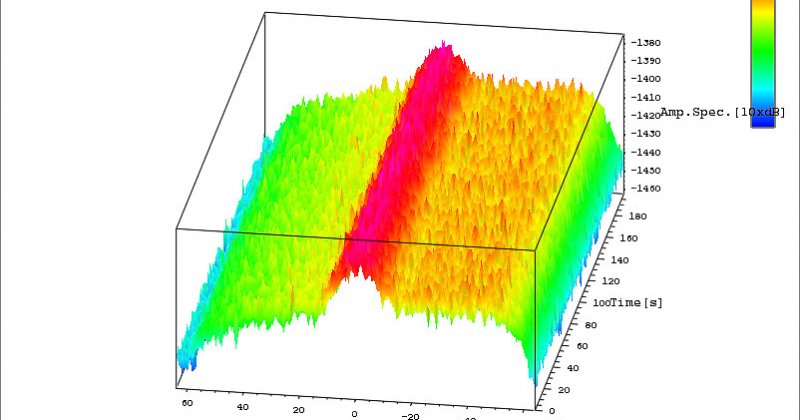
- Detection and localization of interference
- Production of GNSS KPI reports
- GNOME network integration
- Multipath estimations
- Site surveys
- Playback of GNSS data
- Alarm notifications
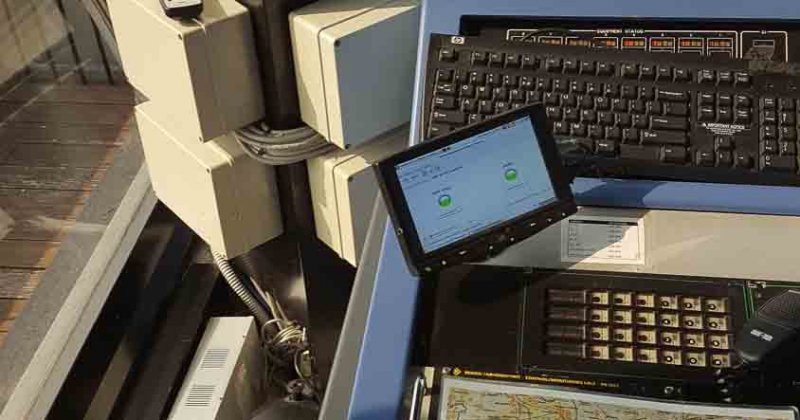
The GNOME system consists of a distributed network of remote sentinels which report the results of their analyses to a common collector, the Central Monitoring Facility (CMF), which operates as a controller and storage as well as a user interface. The CMF has three core modules as well as an optional module.
Core modules:
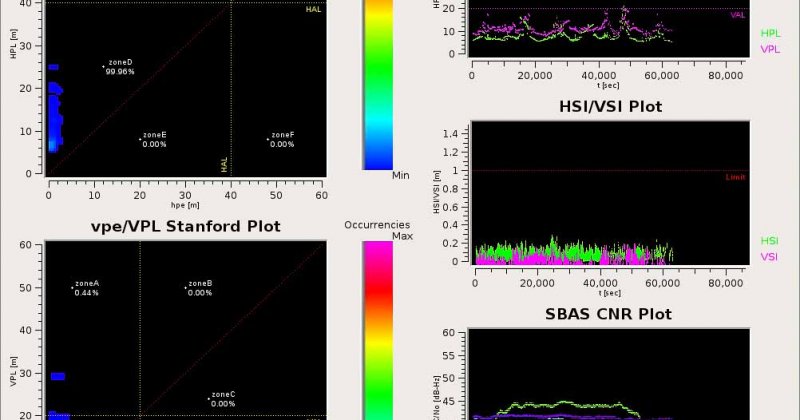
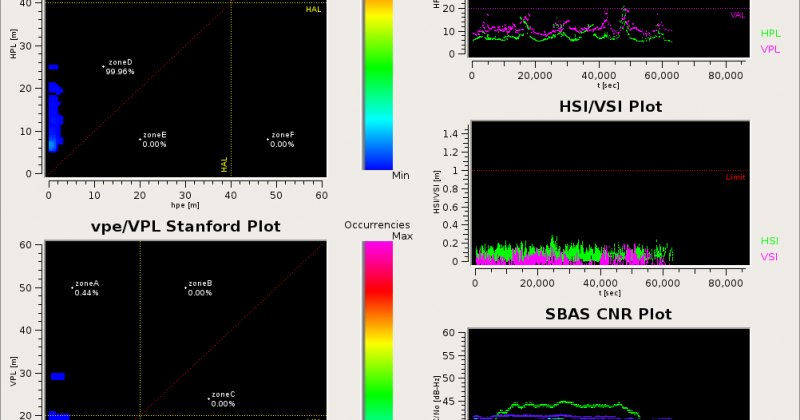
- Real-Time Inspector (RTI): provides continuous visualization of GNSS performance analyses as well as integrity alarms
- Virtual-Time Inspector (VTI): supports post incident/accident investigations and allows play back of data as well as the investigation of anomalies
- Statistical Inspector (StI): processes large observation data sets (up to several months) and generates long-term performance statistics.
Optional module:
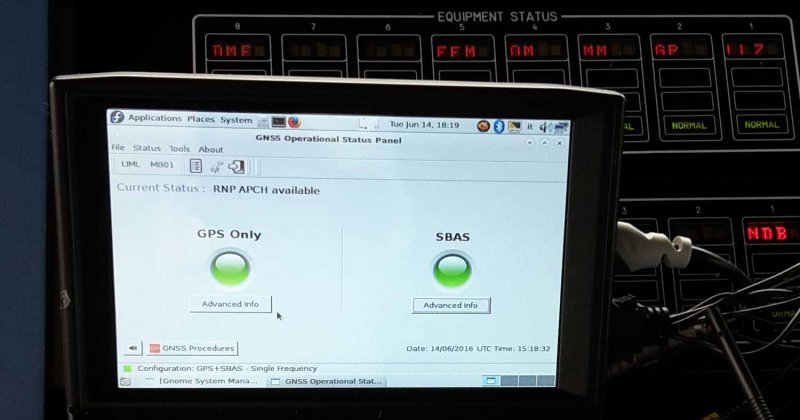
- GNSS Operational Panel (GOSP): provides support to operational ATC personnel in determining GNSS procedure usability. This is done via a panel on the ATC console that displays real-time GNSS status
Error: Contact form not found.